From the Yaozhi Web Liuli
At the opening ceremony of ASCO, Dr. LillianL.Siu was awarded the 2024 DavidA Karnofsky Memorial Award for her outstanding contributions to cancer drug development, clinical trial design and methodology, and the identification of biomarkers for predicting response to immunotherapy. In addition, according to the press release, Dr. Siaw has also been selected as AACR Chairmandesignate for 2024-2025, and she will formally take over the chairmanship at the AACR Annual meeting in April 2025.
On the other hand, domestic research results have increased significantly at this year's ASCO conference. According to the abstract of ASCO2024, about 290 innovative drugs come from about 185 domestic pharmaceutical companies, and more than 50 results have the opportunity to be orally reported, which is the highest in the history.
GSKPD-1 monoclonal antibody: regression of persistence in advanced rectal cancer
GSK announced positive results of its phase II AZUR-1 trial of its PD-1 inhibitor Jemperli (dostarlimab) as monotherapy in locally advanced mismatch repair deficient (dMMR) rectal cancer (abstract number, LBA3512).
The results showed that 100% of 42 patients who received dostarlimab had a clinical complete response (cCR), defined as no evidence of tumor on imaging, endoscopy, or clinical examination. In the first 24 patients, sustained cCR indicated a durable response, with a median follow-up of 26.3 months. Twenty patients had sustained responses lasting at least 12 months without additional treatment. Studies have also found that the level of circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA) is correlated with treatment response and may become an early marker.

Figure 1 Photo source: AndreaCercek oral speech screenshot
These results show a significant efficacy of PD-1 inhibitors alone in patients with locally advanced rectal cancer with dMMR, achieving a pathological complete response that lasts for an extended period of time and obviating the need for further therapy. Although further studies are needed, these results indicate the potential of immunotherapy in the treatment of dMMR rectal cancer, which may replace the traditional standard of chemotherapy and surgery, and reduce the impact of toxic side effects on patients' quality of life. Research is available in the New England paper and the latest news from GSK.
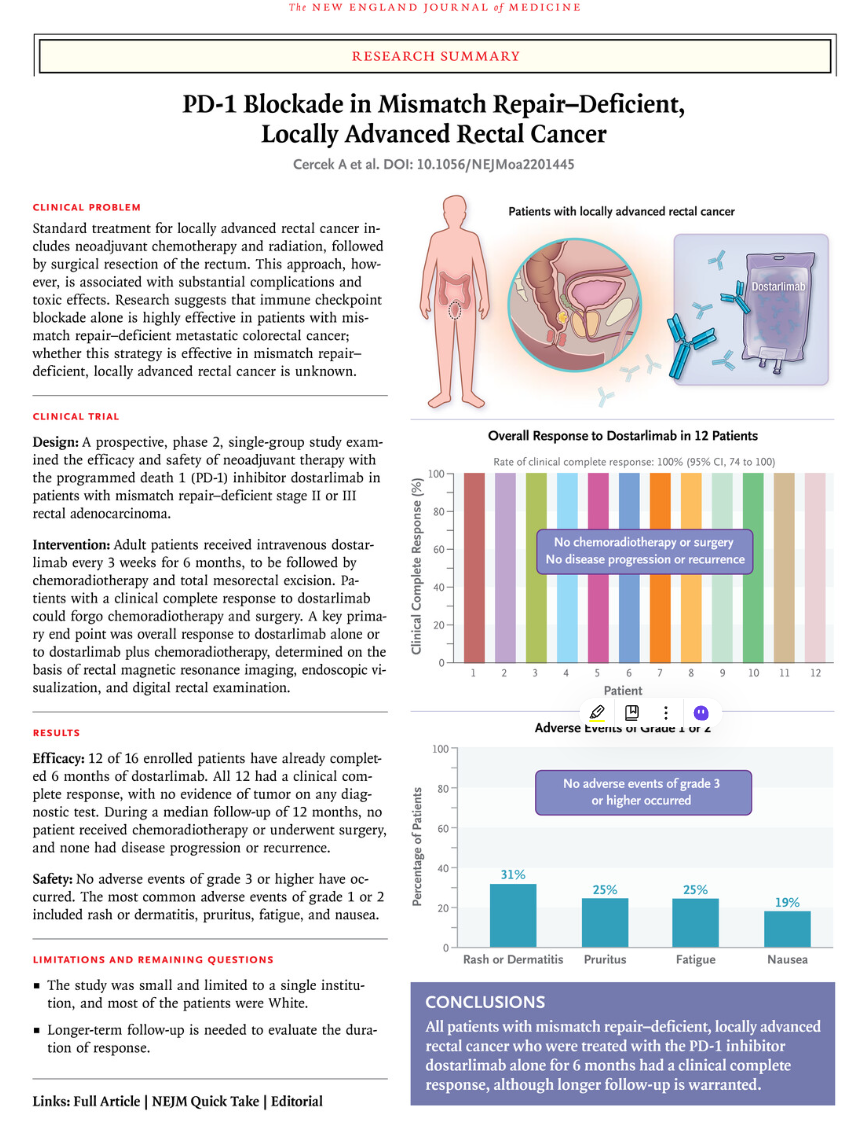
Figure 2 Paper published in the New England Journal
Image source: Reference 3
MAST Study: Metformin may not be beneficial in prostate cancer patients
AnthonyJoshua professor in a conference report called MAST (MetforminActiveSurveillanceTrial) results of a randomized controlled trial the Numbers LBA5002.
In the past, there has been a wealth of epidemiological, biologic, and clinical data suggesting that metformin may affect the progression of low-risk prostate cancer, but this has not previously been evaluated in the context of a randomized controlled trial.
The MAST study investigated the use of metformin to slow or prevent progression in men with low-risk prostate cancer during active surveillance and was designed to prospectively evaluate metformin in men with low-risk prostate cancer eligible for active surveillance.
Patients were eligible if they had been diagnosed with low-risk prostate cancer within the previous 12 months, defined as a Gleason score of less than 6 and involving less than one third of the cores, and a PSA level of less than 10 in any of the cores. These patients were randomly assigned to active surveillance plus placebo or active surveillance plus metformin at an initial dose of 850 mg daily followed by 850 mg daily for 35 months. Assessments including prostate biopsy were performed at baseline, 18 months, and 36 months. A total of 405 patients underwent 1:1 randomization and were well matched for patient characteristics and risk factors. Pathological and therapeutic progress were the primary end points of the study.
The results showed no effect of metformin use on pathology or treatment progression in this population. Although this was not the planned analysis, there are signals that the use of metformin may accelerate progression in certain patients, including those with higher BMI. This study clearly shows that metformin should not be used in men with low-risk localized prostate cancer who are eligible for active surveillance.
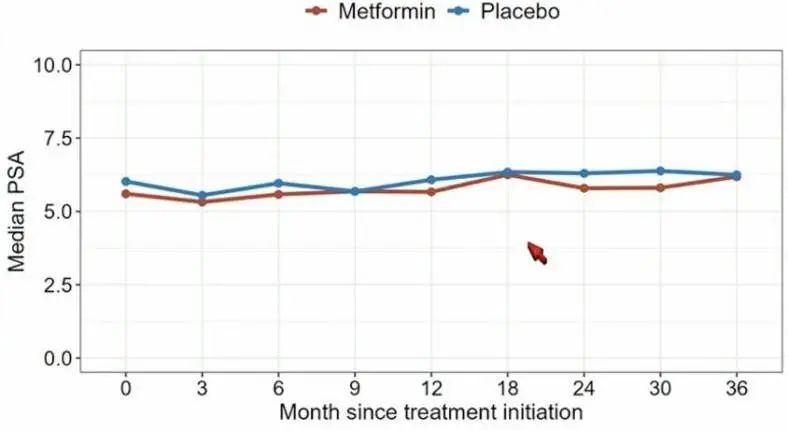
Figure 3 ASCO2024 Prostate Cancer Symposium No statistically significant difference in effect between the metformin and placebo groups.
Photo credit: urotoday.com News Reference 7
CARACO study: Lymph node dissection after chemotherapy does more harm than good
An early study, that LION Ⅲ period test, evaluated the RPLD (RetroperitonealLymphNodeDissection, retroperitoneal lymph node cleaning) to completely after primary surgical resection and lymph node normal in patients with advanced ovarian cancer. In this trial, RPLD did not significantly improve overall or progression-free survival and was associated with a significant increase in severe postoperative complications and 60-day mortality.
The use of neoadjuvant chemotherapy and intermittent surgery has increased significantly in the United States and Europe in recent years, and it is unclear whether RPLD is beneficial for these patients. The phase III CARACO trial was designed to answer this question. This multicenter trial enrolled 379 patients with FIGO stage III-IVA epithelial ovarian cancer, no suspicious retroperitoneal lymph nodes, optimal surgery by primary surgery or intermittent cytoreductive surgery after neoadjuvant chemotherapy, and residual tumor of less than 1cm. Patients were randomized to surgery or no retroperitoneal lymphadenectomy. The primary end point was progression-free survival, and secondary end points included overall survival, safety, surgical results, and quality of life. After surgery, most subjects in both groups had no evidence of residual tumor, and 88% of those who had undergone lymphadenectomy and 86% of those who had not had lymphadenectomy had no evidence of disease. Importantly, the median operative time was 240 minutes for patients who did not undergo lymphadenectomy, compared with 300 minutes for those who underwent lymphadenectomy, meaning that patients who underwent retroperitoneal lymphadenectomy had an extra hour of operative time. Severe morbidity, as assessed by the incidence of blood transfusion or blood loss, reintervention, and urinary tract injury, was significantly improved within 30 days after surgery in both groups. In the intention-to-treat analysis, there was no significant difference in progression-free survival between patients who did not undergo or who underwent retroperitoneal lymphadenectomy, with median progression-free survival of 14.8 months and 18.6 months, respectively, and median overall survival of 48.9 months and 58.8 months, respectively; a subgroup analysis showed no benefit of retroperitoneal lymphadenectomy. Although the results of this study are slightly confounded by failure to reach the target cumulative rate, the data strongly demonstrate that additional surgery and subsequent surgical complications can be avoided in these patients without compromising progression-free or overall survival. Dr. Classe and colleagues wanted to determine whether retroperitoneal lymphadenectomy would be useful in patients with suspicious lymph nodes.
AI patient navigator can help patients who miss colonoscopy revisits
In the U.S., at the Montefeoli Einstein Cancer Center in the Bronx, New York City, which serves predominantly racial and low-income populations, 59% (1,925 of 3276) of patients canceled or did not attend their initial colonoscopy in 2022 despite the guidance of patient navigator. After the efforts of patient navigators, 21% (410) of patients completed colonoscopy, but 1500 patients still missed this critical colorectal cancer screening that year.
At the conference, Dr. AlysonMoadel introduced an AI platform called MyEleanor, Abstract No. 100. In the study, researchers used MyEleanor to serve 2400 patients who missed their colonoscopy appointments between 2022 and 2023. MyEleanor calls patients to discuss rescheduling, assesses barriers to testing, connects patients in real time to clinical staff for quick reappointments, and provides reminders of preoperative preparation. The results showed that MyEleanor was used by 57% of patients who cancelled or did not attend their initial colonoscopy, and 58% of these patients (33% of the total) received a live transfer service to reschedule their examination.
Through MyEleanor, the proportion of patients attending rescheduled appointments among those who did not attend their initial colonoscopy increased from 10% to 19%, and the total number of patients increased by 36%.
Screening barriers data collected by MyEleanor showed that nearly one-third of patients reported at least 2 barriers to booking a colonoscopy, with the main barriers including lack of perceived need, time, distrust of medical care, concern about test results, and cost. Additional studies are planned to explore the impact of the tool on patient compliance, employee burden, and income.
As data on the potential application of AI in the cancer care ecosystem accumulate, it is worth looking forward to how such tools can effectively improve prevention and early detection rates and address gaps in cancer care.
Summary
With the successful conclusion of ASCO2024, we have witnessed a series of exciting advances in cancer treatment. From the breakthrough of innovative drugs to the in-depth exploration of AI medicine, each research result is bringing new hope to patients. We will continue to follow the latest developments in the field of cancer treatment and share more valuable information and insights.
References:
1. Double the number and hit a new high!https://xueqiu.com/9517383519/291853631
2. 2024ASCO Opening Ceremony | Symphony of Science and Art, from cancer care to Cure https://m.163.com/dy/article/J3MVRILF053438SI.html
3. Significant efficacy of PD-1 inhibitor monotherapy in locally advanced rectal cancer patients with mismatch repair deficiency (dMMR)https://www.nejm.org/doi/full/10.1056/NEJMoa2201445
4. GSK press release Superior Results for doselinumab:https://www.gsk.com/en-gb/media/press-releases/jemperli-dostarlimab-trial-continues-to-show-unprecedented-results/
5. Study of AI patient navigatorhttps://meetings.asco.org/abstracts-presentations/237871
6. CARACO phase III trial for advanced ovarian cancerhttps://meetings.asco.org/abstracts-presentations/231692
7. ASCO2024 Prostate Cancer Special Reporthttps://www.urotoday.com/conference-highlights/asco-2024/asco-2024-prostate-cancer.html
8. ASCO2024: MAST (Metformin Active Monitoring Trial) studyhttps://meetings.asco.org/abstracts-presentations/239173
9. An exciting 100% response rate with the PD-1 inhibitor dostalimab https://x.com/ArndtVogel/status/1797703583057743900
10. ASCO2024 New drug research framework: domestic ADCs are exciting, and innovative dual antibodies are emerging.
https://data.eastmoney.com/report/zw_industry.jshtml?infocode=AP202405271634710451
Solemnly declare: the copyright of this article belongs to the original author. The reprint article is only for the purpose of disseminating more information. If the author's information is marked incorrectly, please contact us for the first time to modify or delete it.







