From the Yaozhi Web Liuli
In contrast to the more research-oriented presentations of the AACR, ASCO is focusing more on clinical research, with a focus on clinical benefit, toxicity, survival, and other measurable clinical parameters. Every year, ASCO annual meeting will release the latest cancer research results, showcase the most cutting-edge cancer treatment technology, discuss the most popular cancer topics, and provide the most valuable guidance and suggestions for global cancer prevention and treatment.
What are the highlights of the 2024 ASCO meeting? This article will present three selected reports, with more breakthroughs explored in subsequent articles.
CROWN study: longest PFS for ALK+ advanced NSCLC
Pfizer presented the long-term follow-up results of the phase 3 CROWN study in non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) as an oral presentation, abstract number LBA8503. In this five-year phase III trial, lorlatinib, a third-generation ALK inhibitor, demonstrated an extraordinary progression-free survival (PFS) benefit, making it a new first-line treatment option for patients with ALK-positive non-small-cell lung cancer.
The results showed that median PFS in the loratinib group was not reached, while the median PFS in patients treated with crizotinib (xalkori) was only 9.1 months, and the 5-year PFS rate was 60% in the loratinib group and only 8% in the crizotinib group.
Experts expressed shock at the results, calling them "the most significant improvement in progression-free survival in ALK-positive lung cancer." The CROWN trial further revealed that loratinib showed an excellent PFS advantage in patients with and without brain metastases, and the time to brain progression was significantly prolonged, with only a small number of patients having brain progression within 16 months before treatment.
In conclusion, loratinib demonstrated excellent efficacy and is expected to become the first-line standard of care for patients with ALK-positive NSCLC.
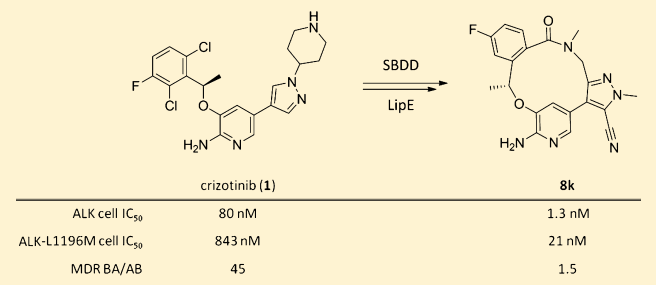
Figure 1 The structure of Lorbrena (PF-06463922), the 8k compound, is a successful example of modification using structure-based drug design.
Image source: Reference 3
ASC4FIRST: Scemblix is expected to become a new standard of care for first-line CML
Novartis has published an update on chronic myeloid leukemia, abstract No. LBA6500. With the new leukemia data, Novartis hopes asciminib (Scemblix) will completely replace the first-generation TKI Gleevec. In the phase III ASC4FIRST study, investigators evaluated asciminib combined with existing tyrosine kinase inhibitors (Tkis) (imatinib, nilotinib, dasatinib, and bosutinib) versus imatinib alone in newly diagnosed Philadelphia chromosome-positive chronic myeloid leukemia in the chronic phase (Ph+CML-CP). This large study, conducted in 29 countries, showed that asciminib significantly improved progression-free survival (PFS) and major molecular response rate (MMR). MMR can reflect whether treatment is expected to eliminate leukemia. This measure measures BCR-ABL1 levels in blood and is more precise than the bone marrow or radiographic response detected by typical tumor response rate endpoints. Three years ago, Scemblix received conditional approval for third-line CML treatment based on MRR data. Overall survival and progression-free survival are widely considered the gold standard in oncology therapy, but for chronic diseases such as CML, deep molecular response and tolerability may be equally important.
The ASC4FIRST study found that the MMR rate at week 48 was 68% in patients receiving asciminib compared with 49% in the other drug arms. In addition, the rate of deep molecular response (MR4) was 39% in the asciminib group, which was higher than 21% in the other drug groups.
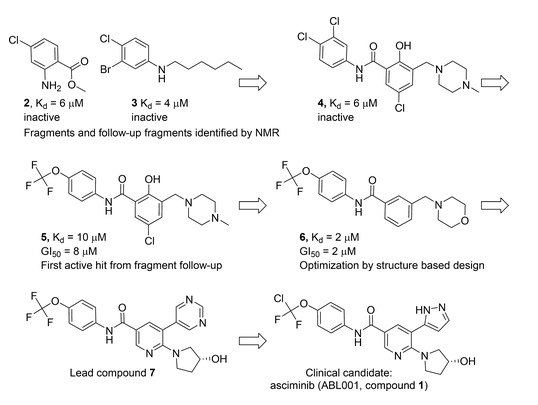
Figure 2 The success of Asciminib was based on step-by-step optimization of the FBDD from fragment screening to clinical candidates: the fragment compound bound to the pocket by means of NMR, 6 optimization to the lead compound, 7 and the final clinical candidate asciminib.
Image source: Reference 5
Randomized GHSGHD21 trial: ADC drug Adcetris is expected to be a new option for lymphoma treatment
Dr. PeterBorchmann of the German Hodgkin Research Group (GHSG) presented the results of a large international randomized trial evaluating the tolerability and efficacy of BrECADD versus BEACOPP in patients with advanced classical Hodgkin's lymphoma, abstract No. LBA7000.
Because Hodgkin's lymphoma mainly affects young people in their 20s and 30s, clinical trials in recent years have focused on achieving high disease control rates while reducing the short - and long-term toxicity associated with conventional chemotherapy and radiotherapy regimens, especially reducing the risk of secondary malignancy and impaired reproductive function among long-term survivors.
Based on a previous study, the investigators modified the upgraded BEACOPP regimen (eBEACOPP, i.e., increasing doses of bleomycin, etoposide, doxorubicin, cyclophosphamide, vincristine, procarbazine, prednisone), in combination with the ADC drug Adcetris(brentuximabvedotin), To reduce overall treatment time and toxicity. This new protocol is called BrECADD and was compared with an upgraded version of BEACOPP in the randomized trial HD21.
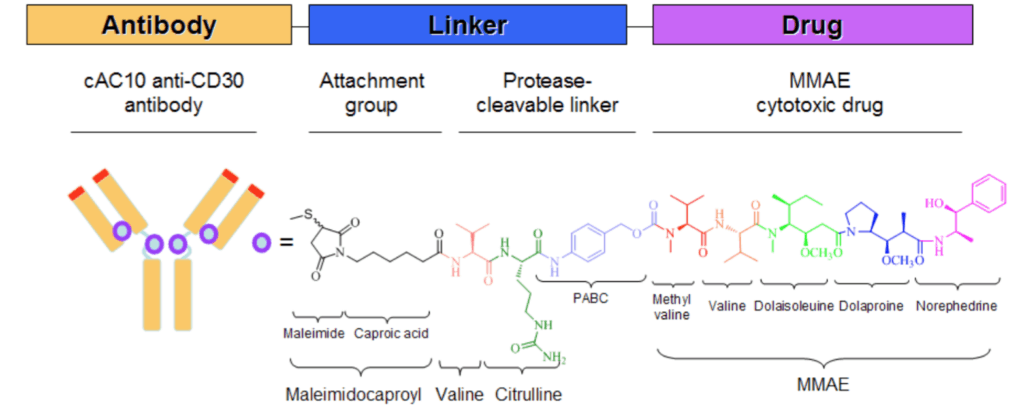
Figure 3 Adcetris is an ADC drug product developed by Takda that consists of an antibody cAC10 that specifically recognizes human CD30, a highly potent antimicrotubule agent monomethyloritatin E (MMAE), and a protease cleavable linker that covalently links the MMAE to cAC10.
Image source: Reference 7
Patients received 4 or 6 cycles of treatment based on disease response in the first two cycles as assessed by interim PET scans. 1482 patients were randomized, 740 to the upgraded BEACOPP and 742 to BrECADD, with a median follow-up of 48 months. The 4-year rate of progression-free survival was 94.3% in the BrECADD group and 90.9% in the BEACOPP group, with a hazard ratio of 0.66. 64% of patients in the BrECADD group had a negative PET scan after 2 cycles of treatment and therefore received only 4 cycles of treatment, significantly reducing the risk of toxicity.
Of note, treatment-related toxicity was lower in the BrECADD group, particularly in terms of hematologic toxicity and peripheral sensory neuropathy. Female reproductive toxicity was lower in the BrECADD group, with more than 95% of women having normal FSH levels after 1 year of treatment compared with 73% in the upgraded BEACOPP group. Dr Borchmann also noted that male reproductive function was better in the BrECADD group, although no detailed data were provided. Although there was no difference in overall survival, this is not unexpected, as effective salvage therapy was available for relapsed patients.
The authors conclude that these results are unprecedented for first-line treatment of Hodgkin lymphoma and that BrECADD should be considered a new standard of care option. Although these results may change clinical practice in some regions such as Europe, the impact in the United States is unclear, as modifications to ABVD regimens, including the addition of brentuximabvedotin and, more recently, nivolumab, have been the subject of recent randomized trials.
These data add more evidence that the majority of patients with advanced Hodgkin lymphoma are curable and that short - and long-term toxicity issues targeting this young patient population are being addressed through multiple strategies.

Figure 4 A poster on tumor biomarker was made by the sub-issue of Nature to welcome ASCO2024.
Photo credit: Nature
Summary
The 2020 ASCO annual meeting shows the latest achievements and standards in the field of oncology. In the following articles, we will share the role of metformin in prostate cancer patients with active surveillance; The possible effects of AI on narrowing disparities in cancer treatment; Surgical approaches for advanced ovarian cancer: innovative surgical techniques and protocols; And advanced colorectal cancer with liver metastasis, welcome to continue to pay attention to the clinical progress of ASCO2024.
References:
1. The 5-year follow-up data of the CROWN trial were released, and the longest PFS related to ALK+ advanced NSCLC was reportedwww.ioncol.com/article/NewsInfo.aspx?id=9728
2. ASCO meeting abstracts LBA8503 website https://meetings.asco.org/abstracts-presentations/232406
3. . Pharmacochemistry of ALK kinase inhibitor Lorlatinib (J. Med. Chem. 2014, 57, 4720−4744) doi: 10.1021/jm500261q
4. ASCO meeting abstracts LBA6500 website https://meetings.asco.org/abstracts-presentations/231667
5. Development of Asciminib (ABL001), an allosteric inhibitor of BCR-ABL1 tyrosine kinase activity (J. Med. Chem. 2018 , 61 , 18 , 8120-8135) doi:10.1021/acs.jmedchem.8b01040
6. ASCO Meeting Abstract No. 11005 https://meetings.asco.org/abstracts-presentations/231637
7. ADC review website https://www.adcreview.com/brentuximab-vedotin-sgn35/
8. Asc-2024 American Society of Clinical Oncology Annual Meeting https://meetings.asco.org/meetings/2024-asco-annual-meeting/316/program-guide/scheduled-sessions/calendar.
Solemnly declare: the copyright of this article belongs to the original author. The reprint article is only for the purpose of disseminating more information. If the author's information is marked incorrectly, please contact us for the first time to modify or delete it.







