Abstract
Glioblastoma is an aggressive tumor that is associated with distinctive infiltrating microglia/macrophages populations. Previous studies demonstrated that chlorogenic acid (5-caffeoylquinic acid, CHA), a phenolic compound with low molecular weight, has an anti-tumor effect in multiple malignant tumors. In the present study, we focused on the macrophage polarization to investigate the molecular mechanisms behind the anti-glioma response of CHA in vitro and in vivo. We found that CHA treatment increased the expression of M1 markers induced by LPS/IFNγ, including iNOS, MHC II (I-A/I-E subregions) and CD11c, and reduced the expression of M2 markers Arg and CD206 induced by IL-4, resulting in promoting the production of apoptotic-like cancer cells and inhibiting the growth of tumor cells by co-culture experiments. The activations of STAT1 and STAT6, which are two crucial signaling events in M1 and M2-polarization, were significantly promoted and suppressed by CHA in macrophages, respectively. Furthermore, In G422 xenograft mice, CHA increased the proportion of CD11c-positive M1 macrophages and decreased the distribution of CD206-positive M2 macrophages in tumor tissue, consistent with the reduction of tumor weight observed in CHA-treated mice. Overall these findings indicated CHA as a potential therapeutic approach to reduce glioma growth through promoting M1-polarized macrophage and inhibiting M2 phenotypic macrophage.
Introduction
Glioblastoma multiforme (GBM) is the most aggressive pattern among brain tumors. GBM has an extremely poor prognosis status: patient survival remains less than 15 months1, even after surgical ablation and routine treatments with chemo- and radio-therapeutic agents. It has been widely shown that the immune microenvironment has a central role in GBM. Microglia/macrophages represent the largest tumor-infiltrating immune cell population, contributing to tumor progression and metastasis2. Thus, a novel research field is focused on immunotherapy-based drug discovery.
Macrophage is broadly categorized as “classically activated” pro-inflammatory M1 macrophages and “alternatively activated” anti-inflammatory M2 macrophages3,4. Macrophages can differentiate into various activation states owing to the cytokine balance in the microenvironment. M1 phenotypic macrophage activation, in response to interferon γ (IFNγ) or lipopolysaccharide (LPS), is characterized by up-regulation of inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) and interleukins IL6 or IL12, and enhancement of the Th1 immune response5,6,7. Alternatively, M2 phenotypic macrophage activation is induced by IL-4 and IL-13 through binding to a common receptor subunit, IL-4Rα, and characterized by increased expression of arginase 1 (Arg1), IL-10 and mannose receptor. In nonmalignant or regressing tumors, the majority of tumor-associated macrophage (TAM) is M1-like, which represents pro-inflammatory activity to kill microorganisms and promote tumor lysis5,7. In malignant tumors, TAM has been shown to be of predominant in M2 phenotype, which has a pro-tumor function by secretion of proangiogenic factors8 and immunosuppressive cytokines9. Increased proportion of M2-type TAM has been associated with poor prognosis in multiple tumors including Hodgkin’s lymphoma, cholangiocarcinoma, breast carcinoma, as well as cerebral glioma10,11,12. Thus, several research groups focused on M2-like TAMs as a potential targets for anticancer therapies and have gained encouraging results. In addition, skewing TAM differentiation away from the M2 to M1 phenotype promoted antitumor immune responses and reduced tumor growth and metastasis in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), prostate cancer, breast cancer and glioblastoma13,14,15,16. Furthermore, M1-type macrophages have been reported to be associated with prolonged survival time in patients with non small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC)17,18.
Some natural compounds and therapeutic drugs have been reported to affect macrophage phenotypic differentiation to exert their antitumor effect. These compounds include the natural products zoledronic acid19 and emodin20, therapeutic monoclonal antibodies including anti-CD4713,21 and the phosphatidylserine-targeting antibody 2aG414, and chemotherapy agents, doxycycline and metformin22,23. Chlorogenic acid (5-caffeoylquinic acid, CHA), the ester formed between caffeic acid and quinic acid24, is a phenolic compound found in the human diet, in coffee, apples, pears and in green tea. It has been shown to have several beneficial biological properties, including anti-bacterial effects, anti-inflammatory effects, and anti-oxidant effects, as well as anti-tumor activities25,26. It has been found to exert anti-inflammatory effects through NF-κB inhibition of prostaglandin E synthesis and cyclo-oxygenase-2 and by suppressing JNK/AP-1 activation27. It has been shown to activate calcineurin and enhance macrophage function in vivo and in vitro28. Furthermore, CHA has been proposed to inhibit tumor growth and angiogenesis by inhibiting tyrosinase and matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-929,30, or by the suppression of HIF-1α stabilizationand AKT phosphorylation31. Recently, published findings from pre-clinical experimental and phase I clinical studies have shown that treatment with CHA has shown therapeutic effects in breast cancer32, brain tumors33, lung cancer34, colon cancer35 and chronic myelogenous leukemia29. However, the molecular mechanisms behind the anti-cancer response of CHA and its effects on macrophage polarization, remains yet largely unclear and need to be clarified.
In this study, we investigate the role of CHA-mediated macrophage polarization in glioblastoma progression. We found that, in vitro, CHA induced LPS/IFNγ- but inhibited IL4-responsive genes through promoting STAT1 signaling and inhibiting STAT6 signaling, respectively. Thereby, CHA promoted the production of apoptotic-like cancer cells and inhibited tumor growth by affecting the interaction between macrophages and cancer cells. We also found that CHA inhibits growth of G422 glioma in vivo, and this effect was associated with a decrease of M2-like TAMs and recruitment of M1-like TAMs into tumor tissue.
Results
CHA promoted M1 polarization of macrophages induced by lipopolysaccharide (LPS) and interferon (IFN)-γ
We detected the effect of CHA on macrophages polarization at the concentrations of 0.5 μM to 5 μM, and the proliferation of macrophages was not affected under these doses of CHA (Supplementary Fig. 1A). Initially, the M1/M2 macrophage phenotype marker genes induced by IFNγ and LPS (M1 inducer) were analyzed using RT-PCR analysis. Treatment with IFNγ/LPS significantly up-regulated the mRNA levels of the M1 marker gene iNOS or IL12 in Ana-1 and RAW264.7 macrophages (P ≤ 0.01). Meanwhile, IFNγ/LPS treatment significantly reduced the mRNA levels of the M2 marker gene Arg1 in Ana-1 cells, but that of RAW264.7 cells was increased (P ≤ 0.01) (Supplementary Fig. 2A,B). Then, at exposure to CHA, IFNγ/LPS-induced iNOS mRNA level was further up-regulated and the Arg1 mRNA level was significantly down-regulated in Ana-1 cells in a concentration-dependent manner (P ≤ 0.05, P ≤ 0.01) (Fig. 1A). Similarly, in RAW264.7 cells, combination with 1 μM of CHA significantly increased the iNOS mRNA level and decreased the Arg1 mRNA level when compared with IFNγ/LPS-treated alnoe (P ≤ 0.05) (Fig. 1B). To further investigate the role of CHA in M1 macrophage differentiation, cell surface markers were assessed by flow cytometry. As shown in Fig. 1C and D, treatment with IFNγ/LPS increased the expression of CD11c and MHC Class II subunits IA/IE, and those were dose and time-dependently increased after combination with CHA in RAW264.7 cells, especially in the expression of CD11c. These results indicated that CHA could promote M1 phenotypic differentiation in macrophages in vitro.
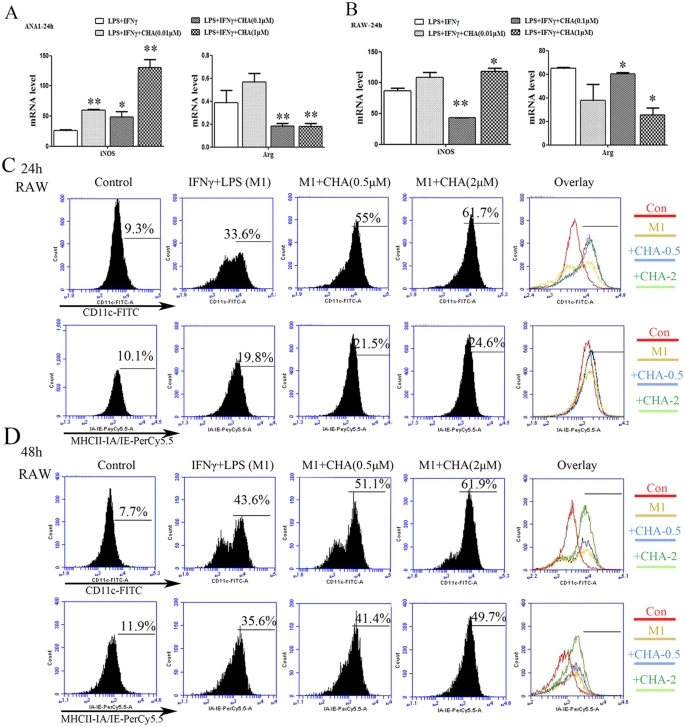
Figure 1: Effect of CHA on macrophage marker expression induced by lipopolysaccharide (LPS) and interferon (IFN)-γ.
Macrophages were treated with LPS (10 ng/ml) and IFNγ (20 ng/ml) with or without different concentrations of CHA for 24 h or 48 h. The mRNA levels of M1-marker gene iNOS and M2-marker gene Arg in Ana-1 (A) and RAW264.7 cells (B) were measured by real-time RT-PCR. The expression of mRNAs was normalized to GAPDH. The expressions of CD11c and MHC Class II IA-IE in RAW264.7 cells for 24 h (C) or 48 h (D) were evaluated by flow cytometry. The histogram bars represent three independent experiments. The data are presented as the mean ± SD. *p-value < 0.05, **p-value < 0.01 vs. LPS/IFNγ.
CHA inhibited M2 polarization of macrophages induced by interleukin (IL)-4
We also analyzed the impact of CHA on M2 polarization of macrophages induced by IL-4. As shown in Supplementary Fig. 2A,B, IL-4 significantly increased the mRNA levels of the M2 marker gene Arg1 or IL10 in Ana-1 and RAW264.7 cells, and reduced the mRNA levels of the M1 marker gene iNOS in Ana-1 cells (P ≤ 0.05, P ≤ 0.01). CHA decreased the expression of the IL-4-induced Arg1 mRNA levels in a dose-dependent manner, but with a significant increase in the iNOS mRNA level at 1 μM of CHA in IL-4 treated Ana-1 cells (P ≤ 0.05) (Fig. 2A). IL-10, another M2 marker gene, was up-regulated by IL-4, which was also found to be dose-dependently inhibited by treatment with CHA in Ana-1 cells (supplementary Fig. 2C). A similar pattern of iNOS mRNA levels was also observed in IL-4-treated RAW264.7 cells at 0.1 or 1 μM of CHA (P ≤ 0.05, P ≤ 0.01) (Fig. 2B). Furthermore, IL-4-induced CD206 expression was decreased by 10% at 2 μM of CHA in Ana-1 cells, but remained unchanged in RAW264.7 cells (Fig. 2C,D). These findings indicated that CHA effectively suppressed M2 phenotypic differentiation in Ana-1 macrophages.
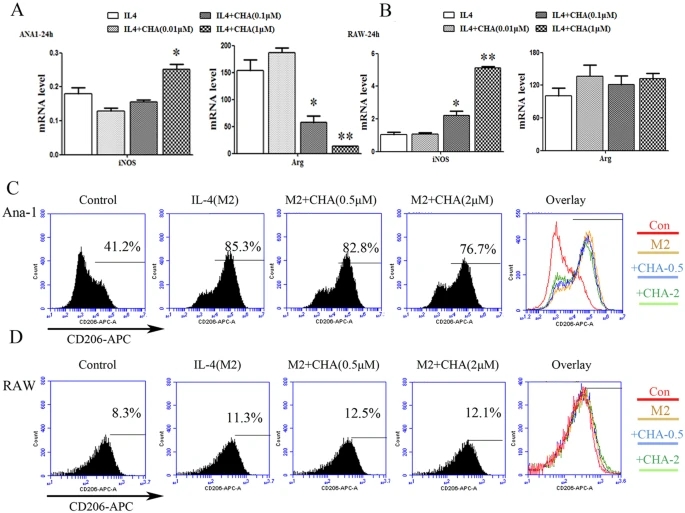
Figure 2: Effect of CHA on macrophage marker expression induced by interleukin (IL)-4.Ana-1 and RAW264.7 cells were treated with interleukin (IL)-4 (20 ng/ml) in the presence of DMSO or different concentrations of CHA for 24 h. The mRNA levels of M1-marker gene iNOS and M2-marker gene Arg in Ana-1 (A) and RAW264.7 cells (B) were measured by real-time RT-PCR. The expression of mRNAs was normalized to GAPDH. The expressions of CD206 in Ana-1 (C) and RAW264.7 cells (D) were evaluated by flow cytometry. The histogram bars represent three independent experiments. The data are presented as the mean ± SD. *p-value < 0.05, **p-value < 0.01 vs.IL-4.CHA regulated macrophage polarization by promoting STAT1 activation and suppressing STAT6 activation
We next sought to investigate the molecular mechanisms of CHA on macrophage polarization. Signal transducer and activator of transcription 1 (STAT1) and STAT6 signaling pathways play critical roles in the M1 and M2 macrophage polarization, respectively36,37. We detected the STAT1 and STAT6 activation after treatment with CHA in M1/M2 inducer stimulated-macrophage. As shown in Fig. 3A,B, the protein expressions of p(Ser727)-STAT1, p(Tyr701)-STAT1 and total STAT1 were significantly upregulated when Ana-1 and RAW264.7 cells were treated with M1-inducer (LPS/IFNγ) (P ≤ 0.01), and phosphor-STAT1 expression was further increased by the administration of CHA, as shown by significant increases in expressions of p(Tyr701)-STAT1 and p(Tyr701)-STAT1/total STAT1 at 1 μM of CHA in Ana-1 cells and by significant induction of p(Ser727)-STAT1 and p(Ser727)-STAT1/total STAT1 in RAW264.7 cells at high dose of CHA (2, 4 μM). Meanwhile, upregulations of p(Tyr641)-STAT6 and p(Tyr641)-STAT6/total STAT6 were observed when Ana-1 or RAW264.7 cells were treated with IL-4 for 24 h, which were significantly reduced by combination with CHA in a dose-dependent manner, particularly in RAW264.7 cells (P ≤ 0.05, P ≤ 0.01) (Fig. 3C,D). These results indicated that CHA could have a regulating effect on macrophage polarization mainly via STAT1 and STAT6 signaling pathways.

Figure 3: Effect of CHA on the STAT signaling pathways in macrophages.
Ana-1 (A) and RAW264.7 (B) cells were treated with lipopolysaccharide (LPS) (10 ng/ml) and interferon (IFN)-γ (20 ng/ml) with or without different concentrations of CHA for 24 h. The expressions of Ser727-phosphorylated STAT1 (p-STAT1ser727), Tyr701-phosphorylated STAT1 (p-STAT1Tyr701) and STAT1were evaluated by a Western blot analysis. Ana-1 (C) and RAW264.7 (D) cells were treated with interleukin (IL)-4 (20 ng/ml) in the presence of DMSO or indicated concentrations of CHA for 24 h. The expressions of Tyr641-phosphorylated STAT6 (p-STAT6Tyr641) and STAT6 were evaluated by a Western blot analysis. The histogram bars represent three independent experiments. The data are presented as the mean ± SD. #p-value < 0.05, ##p-value < 0.01 vs. Con. *p-value < 0.05, **p-value < 0.01 vs. LPS/IFNγ or IL-4.
CHA inhibited the tumor cell growth by affecting the interactions between macrophages and cancer cells
Considering that the highest concentration of CHA used in macrophages polarization did not directly affect the proliferation of tumor cell lines and rodent nerve cells including primary neurons and glial cell lines (CTX and BV2, etc) that could serve as origin of gliomas (Supplementary Fig. 1A–C), we examined whether CHA regulates the interactions between macrophages and brain cancer cells. The proliferation and morphological feature of U87 cells were almost unaffected by treatment with indicated concentrations of CHA, IFNγ/LPS (M1 inducer), or IL-4 (M2 inducer) alone (Supplementary Fig. 3). In the condition of co-culture experiments, the proliferation of U87 cells was increased by co-cultured with M2 inducer-treated macrophages cell lines (RAW264.7 and Ana-1), and this pro-tumor function of the M2 phenotypic macrophages was significantly suppressed by CHA treatment (Fig. 4A–F). Furthermore, we found that the growth of U87 cells was significantly decreased in co-cultured with M1 inducer-treated macrophages (P ≤ 0.05), and the anti-tumor effect of CHA under the assay conditions used was performance in the induction of U87 cells to be as an apoptotic-like shape (Fig. 4A–F). A similar phenomenon was observed when murine forestomach cancer cell MFC-GFP was co-cultured with M1/M2-inducer stimulated macrophages, treatment with 1 μM or 5 μM CHA also decreased the stimulatory role of M2 phenotypic macrophage on tumor growth (Fig. 4G–J). These data indicated that CHA exhibited antitumor effect through intervention of the cell-cell interactions between macrophages and cancer cells.
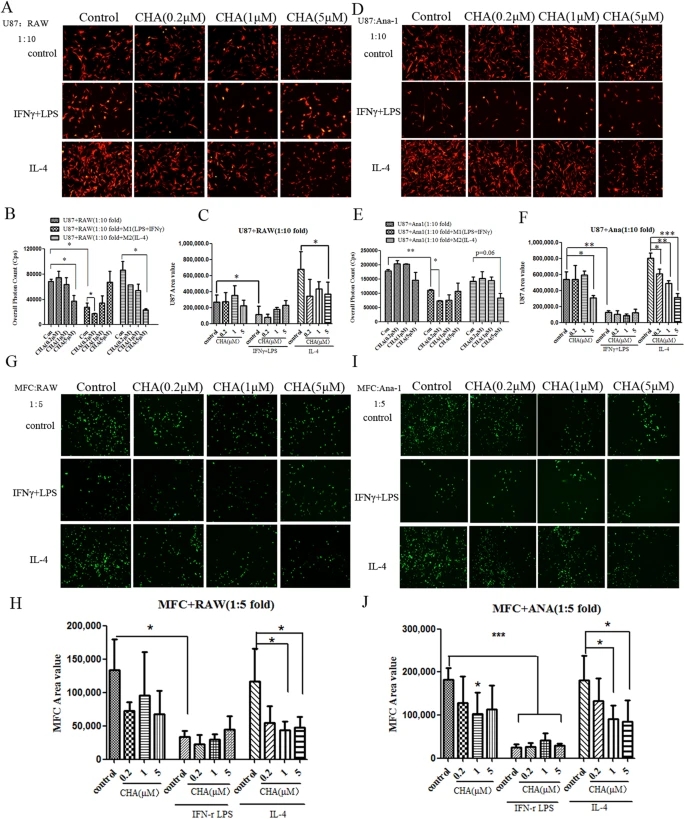
Figure 4: Effect of CHA on tumor cells growth in co-culture of tumor cells with macrophages.Tumor cells (1 × 103) were mono-cultured in lipopolysaccharide (LPS) (10 ng/ml) and interferon (IFN)-γ (20 ng/ml) (M1 stimulator) or interleukin (IL)-4 (20 ng/ml) (M2 stimulator) alone, or in combination with indicated concentration of CHA for 48 h, or were co-cultured with M1 stimulator or M2 stimulator-treated macrophages in the presence of CHA for 48 h. U87-RFP-Luc glioma cells were co-cultured with RAW264.7 (A) or Ana-1 (D) cells, and then tumor cellular morphology was visualized by fluorescence microscopy. The proliferation of U87-RFP-Luc cell was represented as fluorescent area (B,E) or overall photon counts of cells (C,F) by using software of ImageProPlus and EnSpire Multimode Plate Reader, respectively. MFC-GFP forestomach cancer cells were co-cultured with RAW264.7 (G) or Ana-1 (I) cells. The morphology of MFC-GFP cells were visualized by fluorescence microscopy and the proliferation of MFC-GFP cells were assessed by overall fluorescent area of cells using ImageProPlus software (H,J). The histogram bars represent three independent experiments. The data are presented as the mean ± SD. *p-value < 0.05, **p-value < 0.01; as evaluated using Student’s t-test.
CHA inhibited glioma growth in murine model
We next evaluated the anti-cancer effect of CHA using an in vivo xenograft G422 glioma murine model. As shown in Fig. 5A,B, CHA was able to inhibit the tumor growth of G422-bearing mice in a dose-dependent manner without loss of body weight. Tumor inhibition rates were 30% and 48% in the groups treated with 20 mg/kg and 40 mg/kg CHA, respectively (P ≤ 0.05). In addition, flow cytometry analysis was performed to investigate the effects of different phenotypic macrophages infiltrating in tumor tissue after the administration of CHA. Triple immune-staining of CD11c, MHC-II IA/IE and F4/80 results showed that CHA treated G422-bearing mice contained more CD11c+ and MHC-II IA/IE+ double positive cells in F4/80+ macrophages infiltrating in tumor tissue than the control group (Fig. 5C,D). Co-immunostaining of CD206, CD11c and F4/80 showed that the percentages of macrophages expressed CD206 in tumor tissue of CHA-treated mice were fewer than the control group (26.6% in 20 mg/kg group; 8.33% in 40 mg/kg group Vs 63.8% in control group) (Fig. 5E,F). Furthermore, the results from immunofluorescence staining further confirmed the above findings, M1-type macrophages that showed positive staining with antibodies to CD11c and F4/80 were increased in tumor sections from CHA-treated mice (Fig. 5G,I), while M2 macrophages infiltrating into tumor sections that immunostaining with CD206 and F4/80 were significantly reduced by CHA treatment (P ≤ 0.05, P ≤ 0.01) (Fig. 5H,J). Taken together, these results indicated that treatment with CHA significantly reduced the infiltrating M2-type macrophages but increased the M1-type macrophages accumulation in tumor tissue from G422-bearing mice. In addition, in G422 orthotopic glioma model, we found that the slices of intracranial tumor and tumor volume visualized in magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) were decreased after CHA administration (Supplementary Fig. 4A,B).
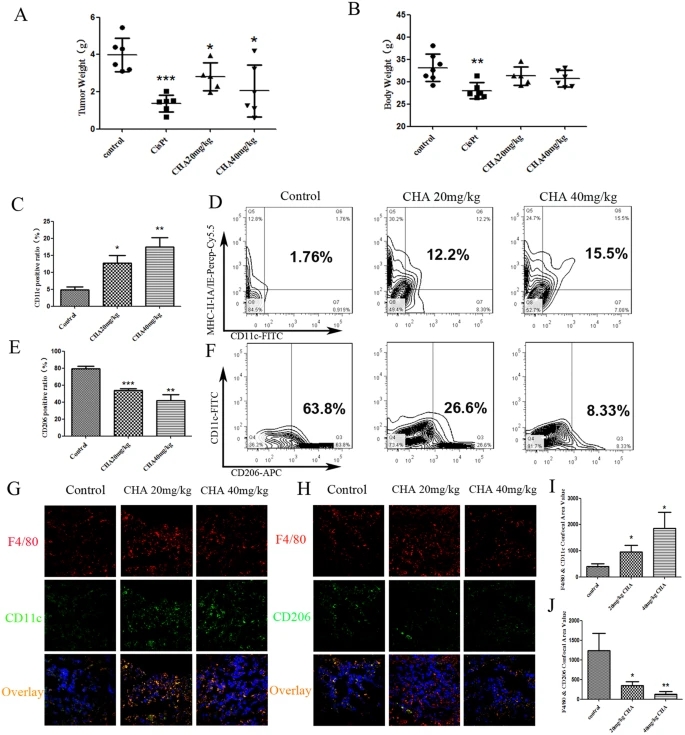
Figure 5: Effect of CHA on glioblastoma progression in G422 xenograft model.
ICR mice were injected subcutaneously in the flank with G422 glioma cells in and were treated with CHA (20 mg/kg or 40 mg/kg per day) for 14 days or cisplatinum (CPT) (6 mg/kg per week). The tumor weight (A) and body weight (B) in individual mice were detected. The infiltration of M1 macrophages (C) in the tumor tissues were evaluated using flow cytometry. The percentage of CD11c, MHC-II IA/IE and F4/80 positive macrophages was presented in the histogram (D). The infiltration of M2 macrophages (E) in the tumor tissues were evaluated using flow cytometry. The percentage of CD206 and F4/80 positive macrophages was presented in the histogram (F). Furthermore, M1 macrophages infiltrating in tumor sections were visualized by immunofluorescence staining of F4/80 and CD11c (G). M2 macrophages infiltrating in tumor sections were visualized by immunofluorescence staining of F4/80 and CD206 (H). The F4/80+CD11c+ area (I) and the F4/80+CD206+ area (J) (% of F4/80+ tumor area) were qualified as area value of overlapping fields. Five random fields from sections of each mouse tumor xenograft were examined. The data are presented as the mean ± SD. *p-value < 0.05, **p-value < 0.01 vs. control.
Discussion
Although CHA has been in phase I clinical trials for multiple types of cancer therapy, little has been reported on the anti-tumor effect of CHA on glioma through modulating macrophage phenotype differentiation. Herein we, for the first time, demonstrated that CHA treatment inhibited anti-inflammatory sate and induced activated macrophage to antitumor pro-inflammatory phenotype, consistent with the inhibition of glioma growth in vitro and in vivo.
The majority of previous studies on CHA have been focused on its direct toxicity to tumor cells. Some research have shown that CHA inhibited tumor growth and tumor angiogenesis in several types of malignancy including glioblastoma through the inhibition of tyrosinase and matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-9 or by induction of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase-dependent apoptosis29,30. In these studies, the effective dose of CHA was more than 10 μM, or reached to 50 μM. In our study, we found that CHA almost did not exhibit direct toxicity towards either of various human cancer cell lines at concentrations lower than 10 μM which is the highest plasma concentration of CHA that achieved in clinical tumor patients following intraperitoneal administration of 3 mg/kg (Supplementary Fig. 1A). Therefore, it is likely that CHA inhibits the growth of glioma predominately through modulating the tumor microenviroment in our study.
In malignant gliomas, there is M2-polarization of microglia acquiring immunosuppressive and tumor-supportive. Inhibition of macrophage differentiation to the M2 phenotype has been proposed to increase the tumor-associated immune response in patients with glioblastoma38. The findings of this study showed that treatment with CHA in glioma-bearing mice inhibited the distribution of M2 type macrophages (F4/80+/CD206+ double labeled cells), consistent with the reduction of tumor weight observed in these mice. Meanwhile, we cannot exclude that, at least in vivo, the CHA-induced phenotype switch to M1 (F4/80+ and CD11c+/MHC-IIIA-IE+) could be secondary effect of the drug on glioma. This is in line with the results in vitro, the up-regulation of anti-inflammatory M2 makers Arg1 and CD206 induced by IL-4 were all reduced upon CHA treatment. And, CHA further increased levels of the pro-inflammatory M1 markers, iNOS, CD11c and MHCIIIA-IE, in the present of LPS/IFNγ treatment.
Increasing evidences have shown that M1-polarized macrophages are likely to play an anti-tumoral response, while M2-polarized macrophages have been associated with malignant tumor growth, angiogenesis, migration and invasion39,40. Such support is new provided by our co-culture experiments, LPS/IFNγ-treated macrophages (M1-type) could inhibit the growth of U87 glioma cells and MFC breast cancer cells, and CHA was able to affect the interaction of M1 macrophages with glioma cells and induced glioma cells toward an apoptotic-like round shape. In contrast, IL-4-treated macrophages (M2-type) promoted the growth of tumor cells, and lower dose (1 μM) of CHA could significantly inhibit the M2 macrophages-induced proliferation of glioma and breast cancer cells. Taken together, these data support the hypothesis that the in vivo and in vitro antitumor effect of CHA depends on the macrophage polarization. We suggested that CHA is not only a potent inhibitor of M2 activation but also an enhancer for M1 activation.
Many studies have revealed the detailed signaling mechanisms of macrophage differentiation. Our finding showed that CHA regulated LPS/IFNγ- and IL-4 responsive genes through promoting STAT1 activation and inhibiting STAT6 activation. In addition to the STAT family, NF-κB, the nuclear receptor PPAR-γ and the CREB-C/EBP axis all participate in macrophage polarization36,41. Previously, CHA has also been reported to exert anti-inflammatory activities in LPS-treated RAW264.7 cells via attenuating the activation of inflammatory signaling pathways NF-κB and JNK/AP-127,42. In our preliminary data, NF-κB activation was not changed by CHA (data not shown). There is still some controversy in the regulatory role of NF-κB on macrophage polarization. Some paper reported that NF-κB signaling mediated M1 phenotype differentiation. NF-κB drives the transcription of many pro-inflammatory genes in macrophages, such as IL-12p40, NOS2 and STAT1/243. S. Gao and S. Iwanowycz, et al. have reported that several Chinese herb-derived antioxidants, such as Curcumin and Emodin, could suppress the excessive response of M1 macrophages via blockade of NF-κB signaling pathway20,44,45,46,47. But others indicated that NF-κB activation plays an important role in macrophage differentiation toward the M2 phenotype. For instance, Y. Fujiwara and colleagues reported that corosolic acid suppresses the M2 polarization of macrophages and tumor cell proliferation by inhibiting both STAT3 and NF-κB activation48. Furthermore, the direct molecular targets of CHA in macrophages in the context of cancer warrant further identification.
In conclusion, we demonstrated that CHA inhibited the growth of glioblastoma in vivo and in vitro at least partially through inhibiting M2 polarization and further skewing macrophage polarization away from the M2- to M1-like phenotype via promotion of STAT1 activation and inhibition of STAT6 activation, respectively. Overall these findings indicated CHA can be used to mediate macrophage polarization to carry out its anti-glioma function.
References
1. Stupp, R. et al. Radiotherapy plus concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide for glioblastoma. The New England journal of medicine 352, 987–996 (2005).
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
2. Lorger, M. Tumor microenvironment in the brain. Cancers 4, 218–243 (2012).
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
3. Benoit, M., Desnues, B. & Mege, J. L. Macrophage polarization in bacterial infections. J Immunol 181, 3733–3739 (2008).
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
4. Mantovani, A. & Sica, A. Macrophages, innate immunity and cancer: balance, tolerance, and diversity. Current opinion in immunology 22, 231–237 (2010).
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
5. Allavena, P., Sica, A., Solinas, G., Porta, C. & Mantovani, A. The inflammatory micro-environment in tumor progression: the role of tumor-associated macrophages. Critical reviews in oncology/hematology 66, 1–9 (2008).
6. Stout, R. D. et al. Macrophages sequentially change their functional phenotype in response to changes in microenvironmental influences. J Immunol 175, 342–349 (2005).
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
7. Mills, C. D., Kincaid, K., Alt, J. M., Heilman, M. J. & Hill, A. M. M-1/M-2 macrophages and the Th1/Th2 paradigm. J Immunol 164, 6166–6173 (2000).
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
8. Murdoch, C., Muthana, M., Coffelt, S. B. & Lewis, C. E. The role of myeloid cells in the promotion of tumour angiogenesis. Nature reviews. Cancer 8, 618–631 (2008).
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
9. Mantovani, A., Sozzani, S., Locati, M., Allavena, P. & Sica, A. Macrophage polarization: tumor-associated macrophages as a paradigm for polarized M2 mononuclear phagocytes. Trends in immunology 23, 549–555 (2002).
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
10. Steidl, C. et al. Tumor-associated macrophages and survival in classic Hodgkin’s lymphoma. The New England journal of medicine 362, 875–885 (2010).
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
11. Chen, J. et al. CCL18 from tumor-associated macrophages promotes breast cancer metastasis via PITPNM3. Cancer cell 19, 541–555 (2011).
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
12. Ye, X. Z. et al. Tumor-associated microglia/macrophages enhance the invasion of glioma stem-like cells via TGF-beta1 signaling pathway. J Immunol 189, 444–453 (2012).
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
13. Zhang, M. et al. Anti-CD47 Treatment Stimulates Phagocytosis of Glioblastoma by M1 and M2 Polarized Macrophages and Promotes M1 Polarized Macrophages In Vivo . PloS one 11, e0153550 (2016).
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
14. Yin, Y., Huang, X., Lynn, K. D. & Thorpe, P. E. Phosphatidylserine-targeting antibody induces M1 macrophage polarization and promotes myeloid-derived suppressor cell differentiation. Cancer immunology research 1, 256–268 (2013).
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
15. Rolny, C. et al. HRG inhibits tumor growth and metastasis by inducing macrophage polarization and vessel normalization through downregulation of PlGF. Cancer cell 19, 31–44 (2011).
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
16. Coscia, M. et al. Zoledronic acid repolarizes tumour-associated macrophages and inhibits mammary carcinogenesis by targeting the mevalonate pathway. Journal of cellular and molecular medicine 14, 2803–2815 (2010).
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
17. Ma, J. et al. The M1 form of tumor-associated macrophages in non-small cell lung cancer is positively associated with survival time. BMC cancer 10, 112 (2010).
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
18. Ohri, C. M., Shikotra, A., Green, R. H., Waller, D. A. & Bradding, P. Macrophages within NSCLC tumour islets are predominantly of a cytotoxic M1 phenotype associated with extended survival. The European respiratory journal 33, 118–126 (2009).
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
19. Comito, G. et al. Zoledronic acid impairs stromal reactivity by inhibiting M2-macrophages polarization and prostate cancer-associated fibroblasts. Oncotarget doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.9497 (2016).
20. Jia, X. et al. Emodin suppresses pulmonary metastasis of breast cancer accompanied with decreased macrophage recruitment and M2 polarization in the lungs. Breast cancer research and treatment 148, 291–302 (2014).
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
21. Weiskopf, K. et al. CD47-blocking immunotherapies stimulate macrophage-mediated destruction of small-cell lung cancer. The Journal of clinical investigation doi: 10.1172/JCI81603 (2016).
22. Ding, L. et al. Metformin prevents cancer metastasis by inhibiting M2-like polarization of tumor associated macrophages. Oncotarget 6, 36441–36455 (2015).
PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
23. He, L. & Marneros, A. G. Doxycycline inhibits polarization of macrophages to the proangiogenic M2-type and subsequent neovascularization. The Journal of biological chemistry 289, 8019–8028 (2014).
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
24. Boerjan, W., Ralph, J. & Baucher, M. Lignin biosynthesis. Annual review of plant biology 54, 519–546 (2003).
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
25. Xu, Y. et al. Protective effects of chlorogenic acid on acute hepatotoxicity induced by lipopolysaccharide in mice. Inflamm Res 59, 871–877 (2010).
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
26. Zhang, X. et al. Chlorogenic acid protects mice against lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury. Injury 41, 746–752 (2010).
27. Shan, J. et al. Chlorogenic acid inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced cyclooxygenase-2 expression in RAW264.7 cells through suppressing NF-kappaB and JNK/AP-1 activation. International immunopharmacology 9, 1042–1048 (2009).
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
28. Wu, H. Z., Luo, J., Yin, Y. X. & Wei, Q. Effects of chlorogenic acid, an active compound activating calcineurin, purified from Flos Lonicerae on macrophage. Acta pharmacologica Sinica 25, 1685–1689 (2004).
29. Bandyopadhyay, G. et al. Chlorogenic acid inhibits Bcr-Abl tyrosine kinase and triggers p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase-dependent apoptosis in chronic myelogenous leukemic cells. Blood 104, 2514–2522 (2004).
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
30. Jin, U. H. et al. A phenolic compound, 5-caffeoylquinic acid (chlorogenic acid), is a new type and strong matrix metalloproteinase-9 inhibitor: isolation and identification from methanol extract of Euonymus alatus. Life sciences 77, 2760–2769 (2005).
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
31. Park, J. J., Hwang, S. J., Park, J. H. & Lee, H. J. Chlorogenic acid inhibits hypoxia-induced angiogenesis via down-regulation of the HIF-1alpha/AKT pathway. Cell Oncol (Dordr) 38, 111–118 (2015).
32. Xu, R., Kang, Q., Ren, J., Li, Z. & Xu, X. Antitumor Molecular Mechanism of Chlorogenic Acid on Inducting Genes GSK-3 beta and APC and Inhibiting Gene beta -Catenin. Journal of analytical methods in chemistry 2013, 951319 (2013).
PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
33. Belkaid, A., Currie, J. C., Desgagnes, J. & Annabi, B. The chemopreventive properties of chlorogenic acid reveal a potential new role for the microsomal glucose-6-phosphate translocase in brain tumor progression. Cancer cell international 6, 7 (2006).
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
34. Feng, R. et al. Inhibition of activator protein-1, NF-kappaB, and MAPKs and induction of phase 2 detoxifying enzyme activity by chlorogenic acid. J Biol Chem 280, 27888–27895 (2005).
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
35. Matsunaga, K. et al. Inhibitory Effects of Chlorogenic Acid on Azoxymethane-induced Colon Carcinogenesis in Male F344 Rats. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev 3, 163–166 (2002).
36. Lawrence, T. & Natoli, G. Transcriptional regulation of macrophage polarization: enabling diversity with identity. Nature reviews. Immunology 11, 750–761 (2011).
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
37. Welch, J. S. et al. TH2 cytokines and allergic challenge induce Ym1 expression in macrophages by a STAT6-dependent mechanism. The Journal of biological chemistry 277, 42821–42829 (2002).
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
38. Fujiwara, Y. et al. Oleanolic acid inhibits macrophage differentiation into the M2 phenotype and glioblastoma cell proliferation by suppressing the activation of STAT3. Oncology reports 26, 1533–1537 (2011).
39. Sica, A. & Mantovani, A. Macrophage plasticity and polarization: in vivo veritas. The Journal of clinical investigation 122, 787–795 (2012).
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
40. Galdiero, M. R., Garlanda, C., Jaillon, S., Marone, G. & Mantovani, A. Tumor associated macrophages and neutrophils in tumor progression. Journal of cellular physiology 228, 1404–1412 (2013).
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
41. Juhas, U., Ryba-Stanislawowska, M., Szargiej, P. & Mysliwska, J. Different pathways of macrophage activation and polarization. Postepy Hig Med Dosw (Online) 69, 496–502 (2015).
42. Hwang, S. J., Kim, Y. W., Park, Y., Lee, H. J. & Kim, K. W. Anti-inflammatory effects of chlorogenic acid in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated RAW 264.7 cells. Inflammation research : official journal of the European Histamine Research Society... [et al.] 63, 81–90 (2014).
43. Ohmori, Y. & Hamilton, T. A. Requirement for STAT1 in LPS-induced gene expression in macrophages. Journal of leukocyte biology 69, 598–604 (2001).
44. Kim, S. J. Curcumin suppresses the production of interleukin-6 in Prevotella intermedia lipopolysaccharide-activated RAW 264.7 cells. Journal of periodontal & implant science 41, 157–163 (2011).
45. Zhou, Y. et al. Curcumin Modulates Macrophage Polarization Through the Inhibition of the Toll-Like Receptor 4 Expression and its Signaling Pathways. Cellular physiology and biochemistry : international journal of experimental cellular physiology, biochemistry, and pharmacology 36, 631–641 (2015).
46. Gao, S. et al. Curcumin induces M2 macrophage polarization by secretion IL-4 and/or IL-13. Journal of molecular and cellular cardiology 85, 131–139 (2015).
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
47. Iwanowycz, S., Wang, J., Altomare, D., Hui, Y. & Fan, D. Emodin Bidirectionally Modulates Macrophage Polarization and Epigenetically Regulates Macrophage Memory. The Journal of biological chemistry 291, 11491–11503 (2016).
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
48. Fujiwara, Y., Komohara, Y., Ikeda, T. & Takeya, M. Corosolic acid inhibits glioblastoma cell proliferation by suppressing the activation of signal transducer and activator of transcription-3 and nuclear factor-kappa B in tumor cells and tumor-associated macrophages. Cancer science 102, 206–211 (2011).
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
49. Xue, N. et al. Antiproliferative effect of HSP90 inhibitor Y306zh against pancreatic cancer is mediated by interruption of AKT and MAPK signaling pathways. Current cancer drug targets 14, 671–683 (2014).
Acknowledgements
The authors express appreciation and thanks to all of the colleagues in their laboratories. This study was supported by the State Key Laboratory of Bioactive Substances and Functions of Natural Medicines National Science and Technology of China.
Author information
Author notes
1 Nina Xue and Qin Zhou: These authors contributed equally to this work. Authors and Affiliations
2 State Key Laboratory of Bioactive Substances and Functions of Natural Medicines, Institute of Materia Medica, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences and Peking Union Medical College, Beijing, 100050, China
Nina Xue, Qin Zhou, Ming Ji, Jing Jin, Fangfang Lai, Ju Chen, Jiandong Jiang & Xiaoguang Chen
3 Jiuzhang Biochemical Engineering Science and Technology Development Co., Ltd., Chengdu, 610041, Sichuan, China Mengtian Zhang, Jing Jia, Huarong Yang & Jie Zhang
4 Department of Glioma, Beijing Shijitan Hospital, Capital Medical University, Beijing, 100038, China Wenbin Li







