Chlorogenic Acid Relieves the Lupus Erythematosus-like Skin Lesions and Arthritis in MRLlpr Mice
CHA is a phenylpropyl substance synthesized through the shikimic acid pathway. In addition to its anti-tumor, anti-inflammatory, and antioxidant abilities, CHA also has immunomodulatory effects. The aim of the present study is to investigate the therapeutic effects of CHA on the skin damage and arthritis caused by systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) in an MRL/lpr mouse model. In the SLE model, female MRL/lpr mice at the age of 10 weeks old were treated with CHA daily or cyclophosphamide (CTX) weekly via intraperitoneal injection for three months. After treatment, CHA can significantly alleviate the skin and mucous membrane damage caused by SLE and has a certain improvement effect on arthritis. CHA could inhibit dsDNA expression to a certain extent but has no obvious regulation on ANA concentration. The ELISA and BioMAP results indicated that CHA might play an anti-inflammatory role by down-regulating the interleukin (IL)-17 level.
In conclusion, our study demonstrates that CHA can alleviate multiorgan damage in MRL/lpr mice by reducing IL-17.
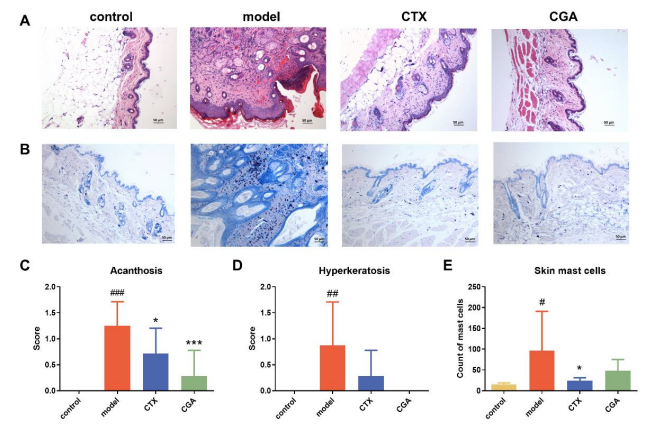
Figure CHA treatment suppressed skin disease in MRL/lpr mice.


